low end tidal co2 after intubation
Measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 has been used to detect accidental esophageal tube placement in noncardiac arrest situations. A right mainstem intubation will also cause a decrease in ETCO2 along with decreased breath sounds on the left side.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC Vasopressors will decrease ETCO2 they cause high afterload increasing BP and myocardial blood flow but a.

. Extraordinarily rarely etCO2 can be slightly higher than arterial CO2 in pregnant patients with otherwise normal lungs. The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg. Other reasons C02 may be low.
After intubation if ETCO 2. A low end-tidal CO 2 in hypothermia In hypothermia the total body CO 2 production is greatly decreased as the metabolic rate is decreased by 6 for every degree below 36. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
Reassess tube placement patency and depth in intubated patients before. A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg.
The PETCO2_1 and PETCO2_2 measurements were statistically significantly different between the patients who survived and those who died p0014 p0015. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. Immediately after intubation etCO2 can help adjust the ventilator settings.
Cardiac arrest decreased cardiac output hypotension cold severe pulmonary edema. Capnography is the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation.
A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. This leads to two foundational principles of etCO2.
Massive pulmonary embolism Contamination of CO 2 detector with gastric contents or acidic drugs including epinephrine administered via the endotracheal tube Severe airway obstruction status asthmaticus. The end-tidal CO2 in these people will be unnaturally low. 3 By the time gas reaches the endotracheal tube the end-tidal CO2 concentration will be lower than the arterial CO2 tension.
End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest. Following intubation adjust the ventilator to target an etCO2 of 30 mm. Over the ensuing minute the patients oxygen saturation declined from 93 to 82 and the end-tidal carbon dioxide decreased to 10 mm Hg.
What should end-tidal CO2 be after intubation. Confirming Maintaining and Assisting Intubation Continuous End Tidal CO2 monitoring can confirm a tracheal intubation. From the time of the esophageal extubation until the next intubation the patient was not ventilated by mask.
After intubation if ETCO 2. This will generally result in a PaCO2 within the normal range 35-45 mm. The Difference Between Arterial and End Tidal CO2.
End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2 first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s. Raising the rate or the tidal volume as well as increasing T low will increase ventilation and decrease CO2. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do.
Immediately after intubation as measured by the capnography the initial PETCO2_1 and at post-ventilation 15 min PETCO2_2 and first second arterial blood gas analysis are recorded. 1 Arterial CO2 should be higher than etCO2. Instances associated with false negative end-tidal CO 2 readings after successful endotracheal intubation also include.
End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output. After intubation if ETCO 2. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa.
What should end-tidal CO2 be after intubation. After intubation if ETCO 2. Breath sounds were distant after the second intubation.
An end-tidal carbon dioxide level of 10 mmHg or less measured 20 minutes after the initiation. The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis.
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST. Consideration has to be made while. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg.
Bhende MS Karasic DG Karasic RB.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Things To Know About Capnography And Advanced Airways Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationinterpreting Waveform Capnography Pearls And Pitfalls Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Icu Nursing Respiratory Care

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Icu One Pager Icu Nurse Critical Care Icu Nursing Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
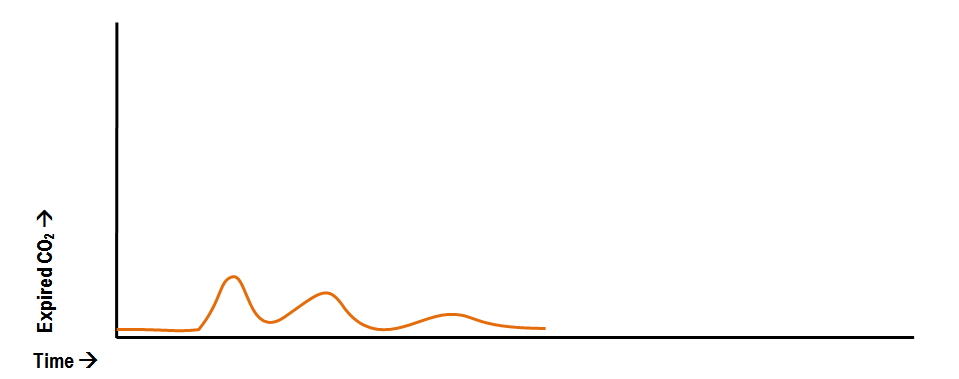
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Pals2000 Pals Rsi Pediatric Nursing Flight Nurse Emergency Nursing

What S In A Wave Form Utilizing End Tidal Capnography For More Than Intubation Confirmation Criticalcarenow
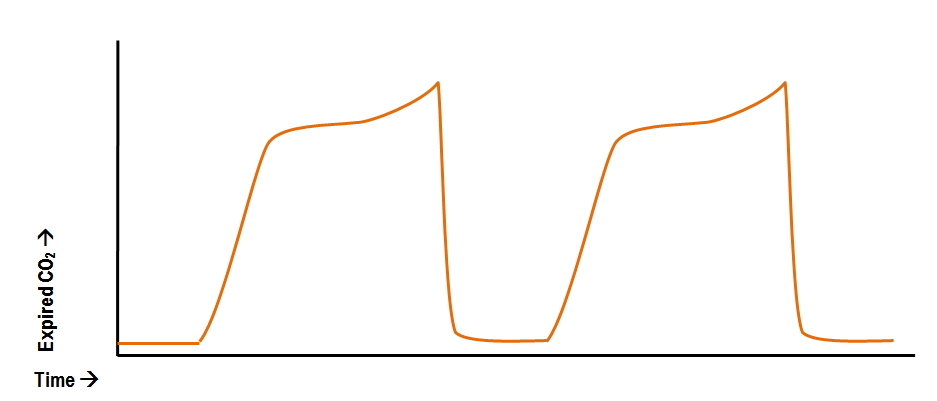
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project


